+37494840986 / +37499016063
Laboratory equipment
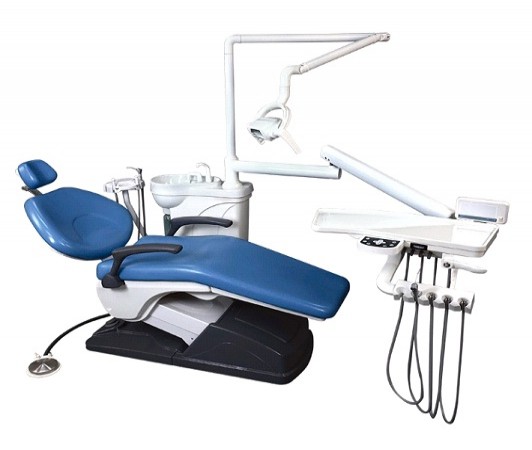
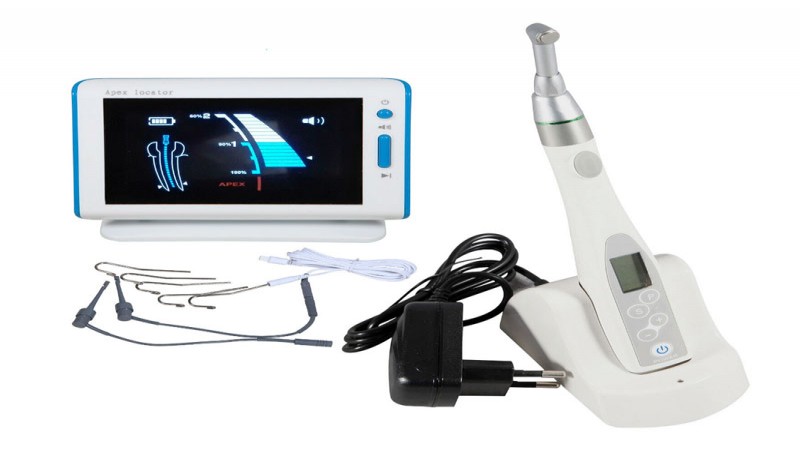
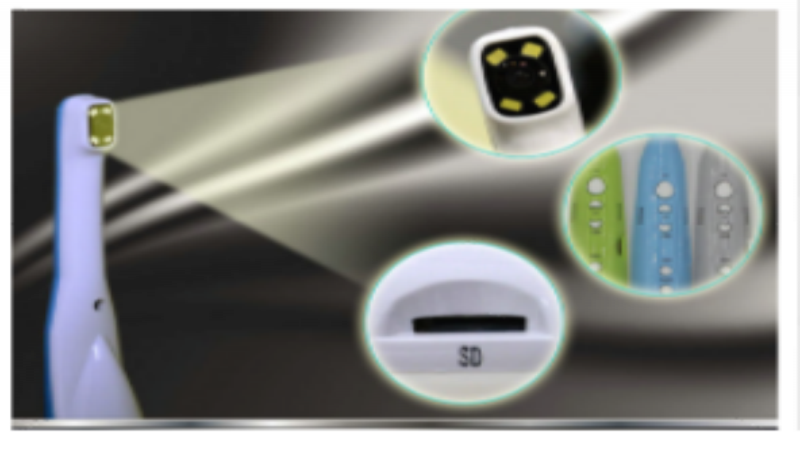
Dental equipment
ENT equipment
Ophthalmological equipment
Sterilization and disinfection
Diagnostic equipment
Gynecological equipment
Dermatological equipment
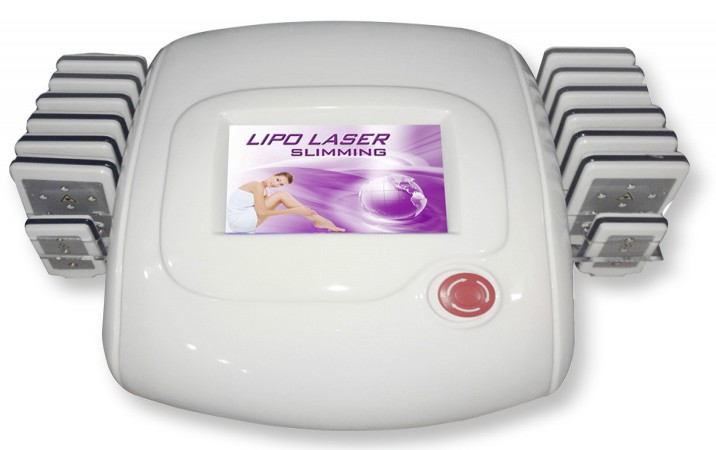
Cosmetology equipment
Surgical Equipment
Pulmonary equipment
Computed tomography CT

 English
English